Explore data below for VEKLURY use and mortality outcomes in patients hospitalized for COVID-19
ACTT-1: pivotal phase 3 clinical trial conducted by the NIH1,2
SOLIDARITY: international, randomized clinical trial conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO)3
Real-world data: large retrospective analysis published in Open Forum Infectious Diseases4,5

-
Median 10 days to recovery with VEKLURY vs 15 days with placebo; recovery rate ratio: 1.29 (95% CI, 1.12 to 1.49), P < 0.001
The primary endpoint was time to recovery within 29 days after randomization
Adverse reaction frequency was comparable between VEKLURY and placebo–all adverse reactions (ARs), Grades ≥3: 41 (8%) with VEKLURY vs 46 (9%) with placebo; serious ARs: 2 (0.4%)* vs 3 (0.6%); ARs leading to treatment discontinuation; 11 (2%)† vs 15 (3%).
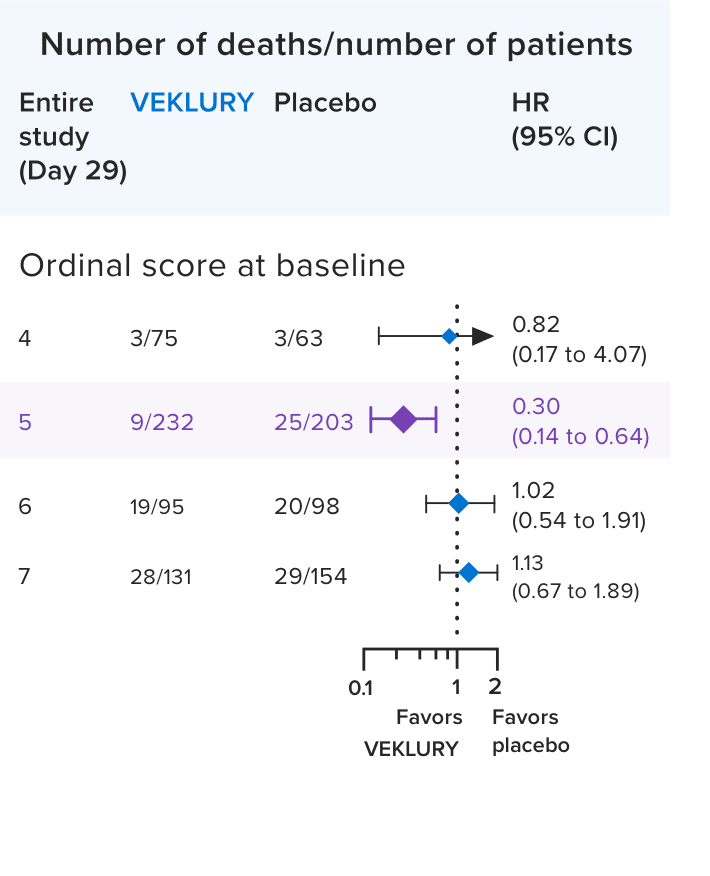
Mortality in the overall population at Day 291,2:
Mortality at Day 29 was a prespecified secondary endpoint.

- Results in the overall population at Day 29 were not statistically significant; ACTT-1 was not powered to evaluate a difference in mortality in the overall population
In a post hoc subgroup analysis, VEKLURY reduced mortality rates at Day 29 in patients on low-flow oxygen at baseline by 70% vs placebo; HR: 0.30 (95% CI, 0.14 to 0.64).2,6
No difference was demonstrated in the other baseline oxygen status subgroups2,6
There was no adjustment to control for multiple testing in this post hoc analysis2
ACTT-1 study design: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 clinical trial in hospitalized adult patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and mild, moderate, or severe COVID-19, who received VEKLURY (n=541) or placebo (n=521) for up to 10 days. Recovery was defined as patients who were no longer hospitalized or hospitalized but no longer required ongoing medical care for COVID-19.1,2
*Seizure (n=1), infusion-related reaction (n=1).
†Seizure (n=1), infusion-related reaction (n=1), transaminases increased (n=3), ALT increased and AST increased (n=1), GFR decreased (n=2), acute kidney injury (n=3).
HR=hazard ratio.

relative risk reduction in mortality was observed in the combined analysis of patients on low- and high-flow oxygen at baseline vs the control arm
- 14.6% with VEKLURY vs 16.3% in the control arm; rate ratio: 0.87 (95% CI, 0.76 to 0.99), P = 0.03; n=5839
- Mortality in the overall population was 14.5% with VEKLURY vs 15.6% in the control arm, which was not statistically significant; rate ratio: 0.91 (95% CI, 0.82 to 1.02), P = 0.12
Study design: The WHO SOLIDARITY trial was an open-label, multicenter, randomized clinical trial that was conducted in 35 countries and enrolled consenting adults (aged ≥18 years) recently hospitalized with, in the view of their doctor, definite COVID-19. The study included 8275 patients who were randomized (1:1) to either receive VEKLURY (n=4146) or to its control (n=4129).* Patients in the VEKLURY arm received a single loading dose of VEKLURY 200 mg IV on Day 1 followed by once-daily maintenance doses of VEKLURY 100 mg IV for up to 9 days unless discharged earlier. The primary outcome was in-hospital mortality, overall, and subdivided by disease. Severity was defined as no oxygen at entry, on oxygen at entry, or already ventilated.†
*All patients were to receive the local standard of care, in addition to any study drugs. Participants were randomly allocated, in equal proportions between the locally available options, to receive whichever of the 4 study drugs (lopinavir, hydroxychloroquine, IFN-β1a, or VEKLURY) were locally available at that time or no study drug (controls).
†The nonventilated supplemental oxygen subgroup comprised the low- and high-flow oxygen subgroups.
IFN-β1a=interferon beta-1a.
Real-world mortality outcomes in patients treated with VEKLURY across variant periods and oxygen subgroups
Mortality study overview4,5,7

A large, real-world, retrospective, comparative effectiveness study examined all-cause in-hospital mortality in adult patients (≥18 years of age) who were treated with VEKLURY vs those not treated with VEKLURY across variant periods pre-Delta (12/2020–4/2021), Delta (5/2021–11/2021), and Omicron (12/2021–4/2022). The study period was from December 2020 to April 2022, which covered the pre-BA4/5 variant period.
The primary outcome was 14-day and 28-day all-cause in-hospital mortality (defined as a discharge status of “expired” or “hospice”).
VEKLURY-assigned patients received at least 1 dose of VEKLURY within 2 days of hospitalization*
Analyses performed based on the supplemental oxygen requirements upon admission and by variant period
This study was sponsored by Gilead Sciences, Inc.
Data source4,5,7
PINC AITM Healthcare Database: This US hospital–based, service-level, all-payer (including commercial, Medicare, Medicaid and other payers) database covered approximately 25% of all US hospitalizations from 48 states.
Study population7
213,264 patient records with a primary COVID-19 diagnosis were analyzed
164,791 VEKLURY patients were matched to 48,473 non-VEKLURY patients (equivalent to 164,791 based on 1:1 matching with replacement) using preferential same-hospital matching.† Postmatching, groups were balanced across baseline supplemental oxygen and variant periods
Key factors that were matched included:
Age
Gender
Race
Ethnicity
Comorbidities
Hospital characteristics
Variant period
Concomitant COVID-19 medications‡
Before matching, compared to non-VEKLURY patients:
VEKLURY patients were younger (46% vs 57% aged ≥65 years)
VEKLURY patients had lower rates of:
Cardiovascular disease (74% vs 83%)
Diabetes (38% vs 41%)
Renal disease (15% vs 30%)
Immunocompromised conditions (23% vs 37%)
VEKLURY patients had a higher rate of obesity (40% vs 32%)
VEKLURY patients were less likely to have/be on:
NSOc (36% vs 48%)
IMV/ECMO (3% vs 4%)
ECMO=extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; IMV=invasive mechanical ventilation; NSOc=no supplemental oxygen charges.
Real-world studies should be interpreted based on the type and size of the source datasets and the methodologies used in order to mitigate potential confounding or bias. Real-world data should be considered in the context of all available data; results may vary between real-world studies.
Strengths4,5
Large sample size from a multicenter database across variant periods
Primary diagnosis for hospitalization was COVID-19
Matching accounted for key factors
Limitations4,5
Potential for residual confounding due to unmeasured variables, including differences in groups that could not be accounted for
The analysis did not account for the following information that was not in the database: time from symptom onset, infecting viral lineages, and prehospital care such as other treatments
Due to the absence of billing charges for supplemental oxygen, some patients who received supplemental oxygen could be misclassified as NSOc
NSOc=no supplemental oxygen charges.
Patients treated early with VEKLURY had significantly reduced mortality across all oxygen subgroups4,5
Mortality reduction at Day 28: VEKLURY (within 2 days of admission) vs matched controls (December 2020–April 2022)
SWIPE FOR MORE >
Significantly lower mortality was observed with patients who were treated with VEKLURY within 2 days of admission for all supplemental oxygen requirements across multiple variant periods vs matched controls who did not receive VEKLURY during hospitalization.
14-day mortality was also statistically significant for all supplemental oxygen requirements across multiple variant periods. In patients treated with VEKLURY, the mortality risk was4,5:
25% lower for those who did not receive supplemental oxygen; aHR: 0.75 (95% CI, 0.68 to 0.83), P < 0.001; n=116,376
28% lower for those on low-flow oxygen; aHR: 0.72 (95% Cl, 0.66 to 0.79), P < 0.0001; n=135,164
17% lower for those on high-flow oxygen or NIV; aHR: 0.83 (95% Cl, 0.77 to 0.89), P < 0.0001; n=69,714
27% lower for those on IMV/ECMO; aHR: 0.73 (95% Cl, 0.65 to 0.82), P < 0.0001; n=8328
SWIPE FOR MORE >
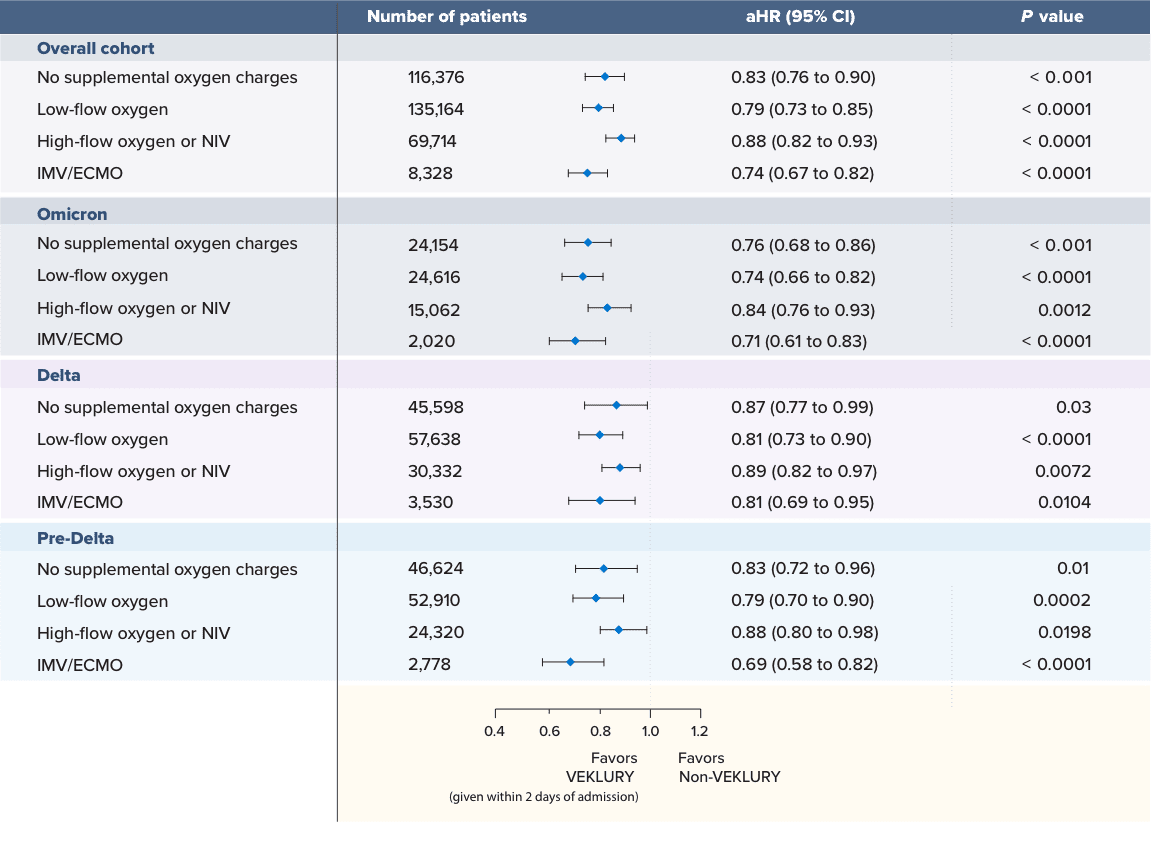
aHR=adjusted hazard ratio; ECMO=extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; IMV=invasive mechanical ventilation; NIV=noninvasive ventilation.
Matched cohort* |
||
| Select characteristics | VEKLURY(n=164,791) | Non-VEKLURY(n=164,791) |
|---|---|---|
| Age group, % | ||
| 18-49 y | 20 | 20 |
| 50-64 y | 32 | 32 |
| 65+ y | 48 | 48 |
| Gender, % | ||
| Female | 48 | 47 |
| Comorbidities, % | ||
| Obesity | 40 | 40 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 26 | 27 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 76 | 76 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 39 | 39 |
| Renal disease | 16 | 17 |
| Cancer | 4 | 4 |
| Immunocompromised condition | 23 | 25 |
| Baseline supplemental oxygen requirements, % | ||
| No supplemental oxygen charges | 35 | 35 |
| Low-flow oxygen | 41 | 41 |
| High-flow oxygen/NIV | 21 | 21 |
| IMV/ECMO | 3 | 3 |
| Variant period, % | ||
| Pre-Delta | 38 | 38 |
| Delta | 42 | 42 |
| Omicron | 20 | 20 |
*All covariates had an absolute standardized difference of <0.15.
ECMO=extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; IMV=invasive mechanical ventilation; NIV=noninvasive ventilation.
“Evidence of the association between [VEKLURY] use and lower mortality rate from this large observational study may inform clinicians in the management of patients with COVID-19 admitted without hypoxemia.”4
View the Open Forum Infectious Diseases publication
Important Safety Information
Important Safety
Information and Indication
Tap for Important Safety Information, including contraindication for history of clinically significant hypersensitivity to VEKLURY.
VEKLURY is indicated for the treatment of COVID-19 in adults and pediatric patients (birth to <18 years of age weighing ≥1.5 kg), who are hospitalized, or not hospitalized, with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 and are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death.
Contraindication
- VEKLURY is contraindicated in patients with a history of clinically significant hypersensitivity reactions to VEKLURY or any of its components.
Warnings and precautions
- Hypersensitivity, including infusion-related and anaphylactic reactions: Hypersensitivity, including infusion-related and anaphylactic reactions, has been observed during and following administration of VEKLURY; most reactions occurred within 1 hour. Monitor patients during infusion and observe for at least 1 hour after infusion is complete for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity as clinically appropriate. Symptoms may include hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, bradycardia, hypoxia, fever, dyspnea, wheezing, angioedema, rash, nausea, diaphoresis, and shivering. Slower infusion rates (maximum infusion time of up to 120 minutes) can potentially prevent these reactions. If a severe infusion-related hypersensitivity reaction occurs, immediately discontinue VEKLURY and initiate appropriate treatment (see Contraindications).
- Increased risk of transaminase elevations: Transaminase elevations have been observed in healthy volunteers and in patients with COVID-19 who received VEKLURY; these elevations have also been reported as a clinical feature of COVID-19. Perform hepatic laboratory testing in all patients (see Dosage and administration). Consider discontinuing VEKLURY if ALT levels increase to >10x ULN. Discontinue VEKLURY if ALT elevation is accompanied by signs or symptoms of liver inflammation.
- Risk of reduced antiviral activity when coadministered with chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine: Coadministration of VEKLURY with chloroquine phosphate or hydroxychloroquine sulfate is not recommended based on data from cell culture experiments, demonstrating potential antagonism, which may lead to a decrease in the antiviral activity of VEKLURY.
Adverse reactions
- The most common adverse reaction (≥5% all grades) was nausea.
- The most common lab abnormalities (≥5% all grades) were increases in ALT and AST.
Dosage and administration
- Administration should take place under conditions where management of severe hypersensitivity reactions, such as anaphylaxis, is possible.
- Treatment duration:
- For patients who are hospitalized, VEKLURY should be initiated as soon as possible after diagnosis of symptomatic COVID-19.
- For patients who are hospitalized and do not require invasive mechanical ventilation and/or ECMO, the recommended treatment duration is 5 days. If a patient does not demonstrate clinical improvement, treatment may be extended up to 5 additional days, for a total treatment duration of up to 10 days.
- For patients who are hospitalized and require invasive mechanical ventilation and/or ECMO, the recommended total treatment duration is 10 days.
- For patients who are not hospitalized, diagnosed with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, and are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death, the recommended total treatment duration is 3 days. VEKLURY should be initiated as soon as possible after diagnosis of symptomatic COVID-19 and within 7 days of symptom onset for outpatient use.
- Testing prior to and during treatment: Perform hepatic laboratory and prothrombin time testing prior to initiating VEKLURY and during use as clinically appropriate.
- Renal impairment: No dosage adjustment of VEKLURY is recommended in patients with any degree of renal impairment, including patients on dialysis. VEKLURY may be administered without regard to the timing of dialysis.
Pregnancy and lactation
- Pregnancy: Available clinical trial data for VEKLURY in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes following second- and third-trimester exposure. There are insufficient data to evaluate the risk of VEKLURY exposure during the first trimester. Maternal and fetal risks are associated with untreated COVID-19 in pregnancy.
- Lactation: VEKLURY can pass into breast milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for VEKLURY and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from VEKLURY or from an underlying maternal condition. Breastfeeding individuals with COVID-19 should follow practices according to clinical guidelines to avoid exposing the infant to COVID-19.
Indication
VEKLURY is indicated for the treatment of COVID-19 in adults and pediatric patients (birth to <18 years of age weighing ≥1.5 kg), who are hospitalized, or not hospitalized, with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 and are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death.
Please see full Prescribing Information for VEKLURY.
*Refer to the Dosage and Administration section of the full Prescribing Information for dosage recommendations.
†If unmatched within the same hospital, patients were matched with other patients of the same age group, supplemental oxygenation status, and 2- to 3-month blocks of admission month from another hospital of the same bed-size category.
‡Other treatments administered at baseline for patients (across both study arms) included anticoagulants, corticosteroids, convalescent plasma, tocilizumab, and baricitinib.
aHR=adjusted hazard ratio; ECMO=extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; IMV=invasive mechanical ventilation; NIV=noninvasive ventilation.
PINC AITM is a trademark of Premier, Inc. (formerly Premier Healthcare Database).

