Explore real-world evidence and guideline recommendations to help optimize treatment decisions with VEKLURY and corticosteroids for your patients hospitalized for COVID-19.
NIH: guideline recommendations for use of VEKLURY and corticosteroids in patients hospitalized for COVID-191
ACTT-1: pivotal phase 3 clinical trial conducted by the NIH2
Real-world data: large retrospective analysis of the impact of VEKLURY + dexamethasone vs dexamethasone alone on inpatient mortality3
COVID-19 is driven by the replication of SARS-CoV-21

When and how long viral replication occurs can vary significantly across patients. Age, underlying conditions, and vaccination status are some factors that can affect viral replication4,5

Viral replication can still occur later in the disease course, even during the inflammatory phase6

Immunosuppressive therapies (eg, corticosteroids) that modulate the inflammatory response may impair viral clearance and extend viral replication1,7
Select guidelines related to the use of VEKLURY and corticosteroids in adult patients hospitalized with COVID-19
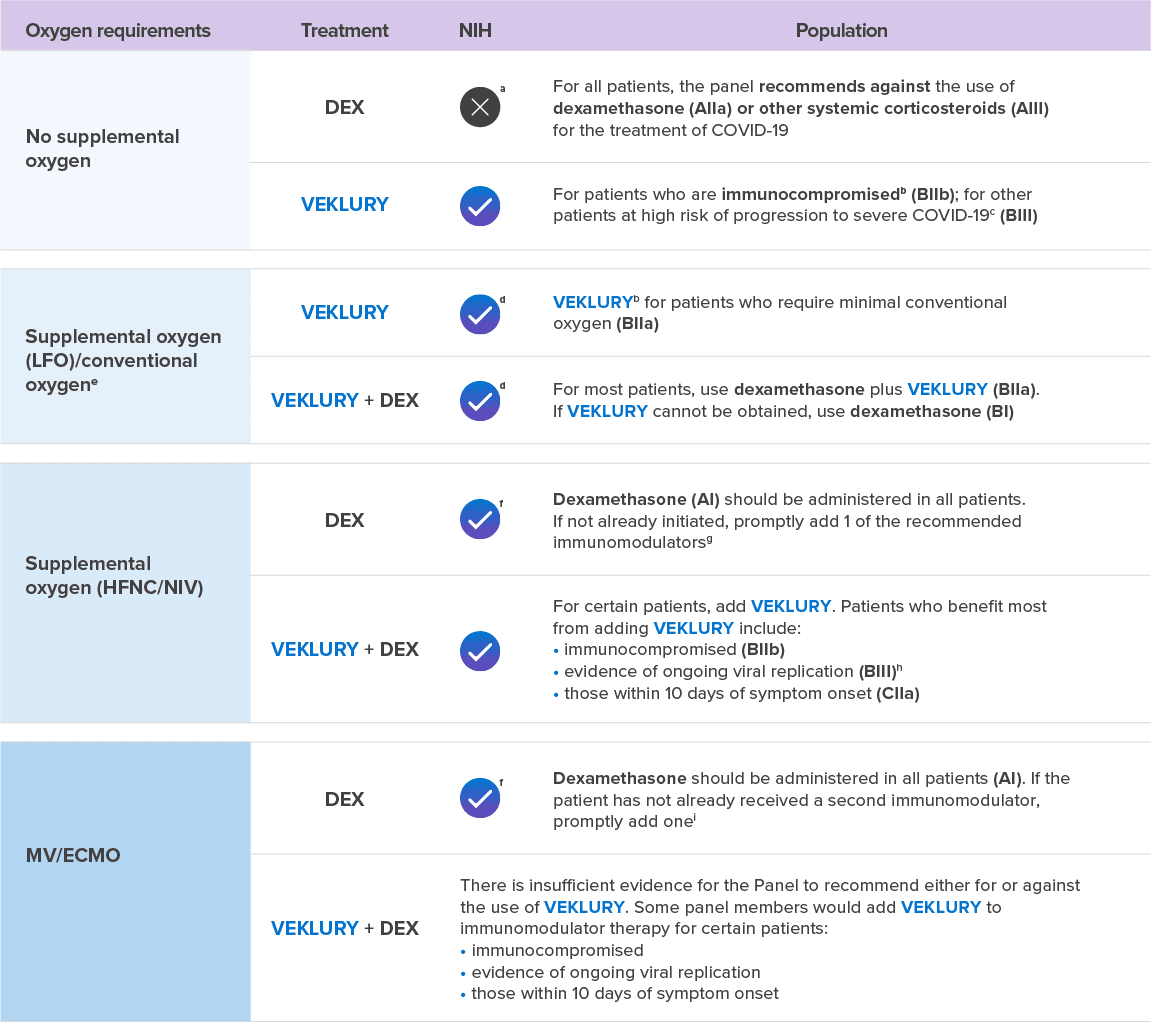
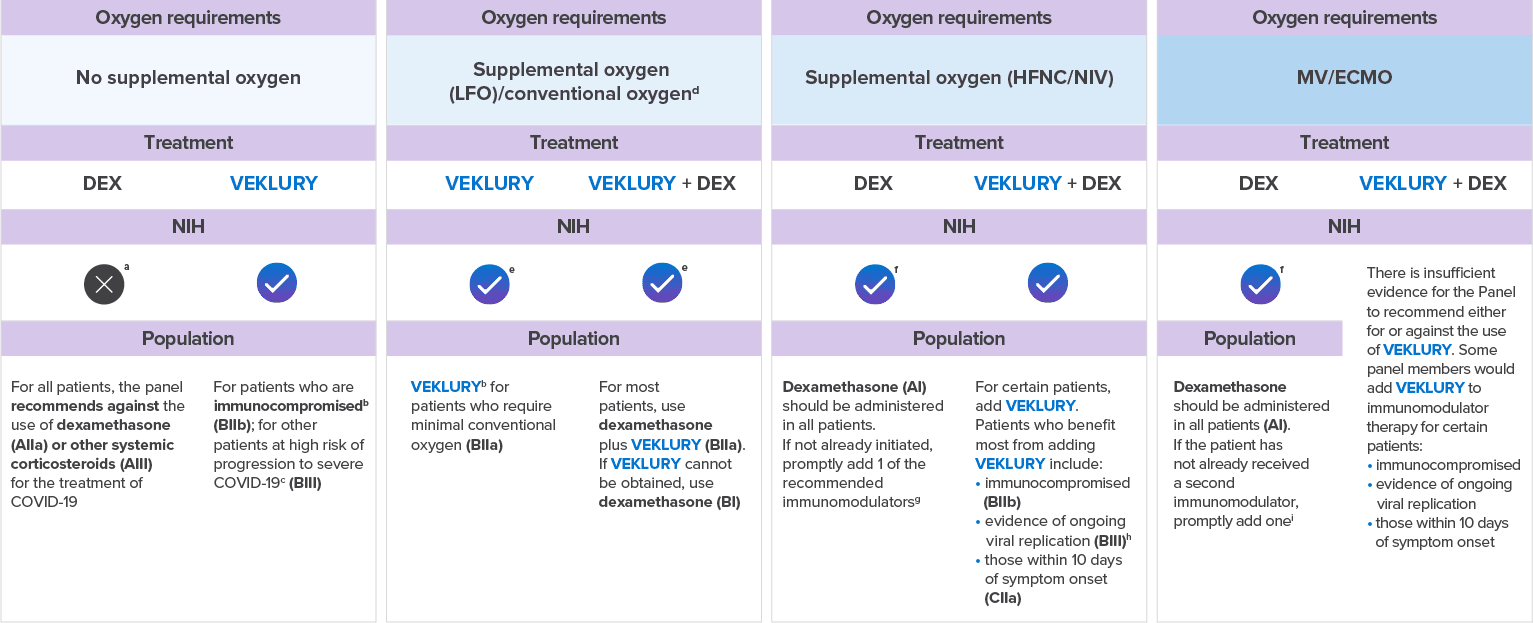
SWIPE FOR MORE >
aCorticosteroids that are prescribed for an underlying condition should be continued.
bEvidence suggests that the benefit of VEKLURY is greatest when the drug is given early in the course of COVID-19 (eg, within 10 days of symptom onset).
cFor a list of risk factors, see the CDC webpage: Underlying Medical Conditions Associated With Higher Risk for Severe COVID-19.
dConventional oxygen refers to oxygen supplementation that is not HFNC oxygen, NIV, MV, or ECMO.
eIf these patients progress to requiring HFNC oxygen, NIV, MV, or ECMO, the full course of VEKLURY should still be completed.
fDexamethasone should be initiated immediately, without waiting until the second immunomodulator can be acquired. If other immunomodulators cannot be obtained or are contraindicated, use dexamethasone
alone (AI).
gPreferred immunomodulator: PO baricitinib (AI); preferred alternative: IV tocilizumab (BIIa); additional alternatives (listed in alphabetical order):
IV abatacept (CIIa), IV infliximab (CIIa).
hEg, those with a low Ct value, as measured by an RT-PCR result or with a positive rapid antigen test result.
iRecommended immunomodulators (listed in alphabetical order): PO baricitinib (BIIa) and IV tocilizumab (BIIa). If PO baricitinib and IV tocilizumab are not available or feasible to use,
PO tofacitinib can be used instead of PO baricitinib (CIIa), and IV sarilumab can be used instead of IV tocilizumab (CIIa).
Strength of Recommendations: A=Strong recommendation for the statement; B=Moderate recommendation for the statement; C=Weak recommendation for the
statement.
Evidence for Recommendation: I: High quality of evidence: 1 or more randomized trials without major limitations,* well-powered subgroup analyses of such trials, or meta-analyses without
major limitations;
IIa: Moderate quality of evidence: Randomized trials and subgroup analyses of randomized trials that do not meet the criteria for a I rating; IIb: Moderate quality of evidence: Observational studies without
major limitations†; III: Expert opinion.
VEKLURY is FDA approved across a spectrum of COVID-19 severity and can be used regardless of a hospitalized patient’s oxygen requirements8
*The rating may be lower than I in cases where trials have produced conflicting results.
‡This category also includes meta-analyses of observational studies.
Ct=cycle threshold; DEX=dexamethasone; ECMO=extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; HFNC=high-flow nasal cannula; LFO=low-flow oxygen; MV=mechanical ventilation; NIV=noninvasive ventilation; PO=oral; RT-PCR=reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction.
In a retrospective real-world study of more than 97,000 US patients who were hospitalized for COVID-19 and received dexamethasone within the first 2 days,

of patients not receiving supplemental oxygen at baseline (n=42,571) were treated with dexamethasone monotherapy (n=15,972) despite the NIH recommendation against its use with these patients. VEKLURY is the only recommended antiviral therapy for adult patients who are hospitalized for COVID-19 and do not require supplemental oxygen.


of patients receiving low-flow oxygen (n=35,768) were treated with dexamethasone monotherapy (n=13,234). The NIH guidelines recommend use of VEKLURY plus dexamethasone for
most patients in this category.

“Many patients are being treated with dexamethasone monotherapy across the range of supplemental oxygen support, including patients with no oxygen support requirements, which goes against…guideline recommendations.”3

-
Median 10 days to recovery with VEKLURY vs 15 days with placebo; recovery rate ratio: 1.29 (95% CI, 1.12 to 1.49), P < 0.001
-
The primary endpoint was time to recovery within 29 days after randomization
Adverse reaction frequency was comparable between VEKLURY and placebo–all adverse reactions (ARs), Grades ≥3: 41 (8%) with VEKLURY vs 46 (9%) with placebo; serious ARs: 2 (0.4%)* vs 3 (0.6%); ARs leading to treatment discontinuation; 11 (2%)† vs 15 (3%).
Steroid-free, post hoc sensitivity analysis from ACTT-12,9

days shorter recovery time with VEKLURY
Median 9 days with VEKLURY, without corticosteroids, (n=327) vs 14 days with placebo, without corticosteroids, (n=283); recovery rate ratio: 1.28 (95% CI, 1.09 to 1.50).
Median 9 days with VEKLURY, without corticosteroids, (n=327) vs 14 days with placebo, without corticosteroids, (n=283); recovery rate ratio: 1.28 (95% CI, 1.09 to 1.50).
-
Patients were censored at earliest reported use of corticosteroids
-
Recovery without prior use of corticosteroids was reported in 327 out of 541 VEKLURY patients and 283 out of 521 placebo patients
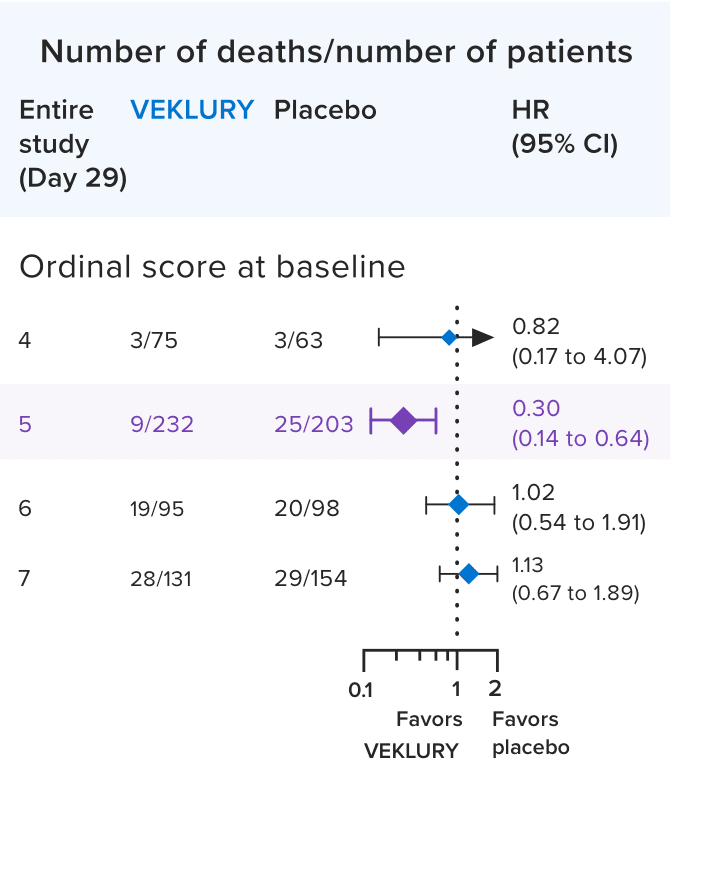
Mortality in the overall population at Day 292,8:
Mortality at Day 29 was a prespecified secondary endpoint.
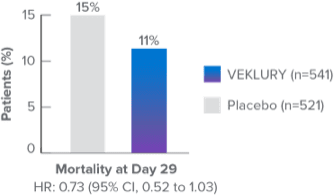
- Results at Day 29 were not statistically significant; ACTT-1 was not powered to evaluate a difference in mortality in the overall population
In a post hoc subgroup analysis, VEKLURY reduced mortality rates at Day 29 in patients on low-flow oxygen at baseline by 70% vs placebo; HR: 0.30 (95% CI, 0.14 to 0.64).2,9
-
No difference was demonstrated in the other baseline oxygen status subgroups2,9
-
There was no adjustment to control for multiple testing in this post hoc analysis2
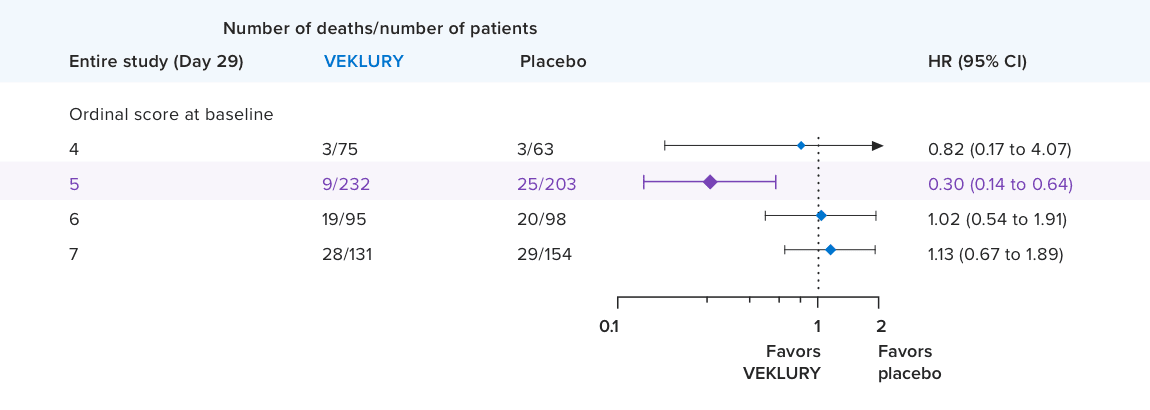
ACTT-1 study design: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 clinical trial in hospitalized adult patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and mild, moderate, or severe COVID-19, who received VEKLURY (n=541) or placebo (n=521) for up to 10 days. Recovery was defined as patients who were no longer hospitalized or hospitalized but no longer required ongoing medical care for COVID-19.2,8
-
23% of patients treated with VEKLURY or placebo as planned also received corticosteroids2
*Seizure (n=1), infusion-related reaction (n=1).
†Seizure (n=1), infusion-related reaction (n=1), transaminases increased (n=3), ALT increased and AST increased (n=1), GFR decreased (n=2), acute kidney injury (n=3).
HR=hazard ratio.
Real-world mortality study: VEKLURY + dexamethasone compared to dexamethasone alone in patients hospitalized for COVID-193
Study overview3

A large, real-world, retrospective, comparative effectiveness study examined all-cause inpatient mortality in adult patients (≥18 years of age) who were treated with VEKLURY + dexamethasone or dexamethasone alone across the Omicron variant period (12/2021–4/2023). The primary endpoints were 14-day and 28-day all-cause inpatient mortality (defined as a discharge status of “expired” or “hospice”).
-
All patients received at least 1 dose of dexamethasone within 2 days of hospitalization
-
Patients treated with VEKLURY + dexamethasone also received at least 1 dose of VEKLURY within 2 days of hospitalization*
-
All analyses were stratified by baseline supplemental oxygen requirements
-
This study was sponsored by Gilead Sciences, Inc.
Data source3,10
PINC AITM Healthcare Database: This US hospital–based, service-level, all-payer (including commercial, Medicare, Medicaid, and other payers) database covered approximately 25% of all US hospitalizations across 48 states.
Study population3
-
After 1:1 matching without replacement, 33,037 VEKLURY + dexamethasone patients were matched to 33,037 dexamethasone monotherapy patients†
-
Postmatching, groups were balanced across baseline supplemental oxygen use
Key factors that were matched included:
- Age
- Gender
- Comorbidities
- Ethnicity
- Hospital characteristics
- Baseline supplemental oxygen
- Concomitant treatments used‡
Before matching, compared to the dexamethasone monotherapy cohort:
VEKLURY + dexamethasone patients had lower rates of:
Renal disease (23% vs 36%)
Diabetes (38% vs 42%)
VEKLURY + dexamethasone patients were younger (67% vs 70% aged ≥65 years)
VEKLURY + dexamethasone patients were more likely to have/be on:
Low-flow oxygen (37% vs 36%)
High-flow oxygen/NIV (18% vs 16%)
VEKLURY + dexamethasone patients were less likely to have/be on:
NSOc (43% vs 44%)
IMV/ECMO (2% vs 4%)
NIV=noninvasive ventilation.
Real-world studies should be interpreted based on the type and size of the source datasets and the methodologies used in order to mitigate potential confounding or bias. Real-world data should be considered in the context of all available data; results may vary between real-world studies
Strengths3
Large study population with COVID-19 diagnosis present on admission from a multicenter administrative database
Complements and builds on the findings from other RCTs and subsequent research over the evolution of the COVID-19 era
Two well-established methods were applied, PSM and IPTW, to balance inherently different groups due to confounding by indication; consistent results were obtained with the 2 methods
Limitations3
Potential for residual confounding due to imbalances in unmeasured variables between the treatment groups even after PSM
Data on time of symptom onset or time since first positive COVID-19 test were not available
No vaccination data were available in the database
Patients from hospitals that did not report any charges for low-flow oxygen were not included in the NSOc group to ensure that data were from hospitals that uniformly report supplemental oxygen requirements
-
Data on antiviral use or any other treatment administered prior to hospitalization were unavailable, which may have led to residual confounding
IPTW=inverse probability of treatment weighting; PSM=propensity score matching; NSOc=no supplemental oxygen charges; RCT=randomized controlled trial.
Patients treated with VEKLURY + dexamethasone had a significantly reduced mortality risk vs dexamethasone alone3
Mortality reduction at Day 28 observed with VEKLURY + dexamethasone vs dexamethasone monotherapy (December 2021–April 2023)
Even across all baseline supplemental oxygen requirements, significant reduction in 28-day mortality was observed with VEKLURY + dexamethasone vs dexamethasone alone (within 2 days of admission)
SWIPE FOR MORE >
Reduction in 28-day mortality risk by supplemental oxygen subgroup: VEKLURY + dexamethasone vs dexamethasone monotherapy (December 2021–April 2023)
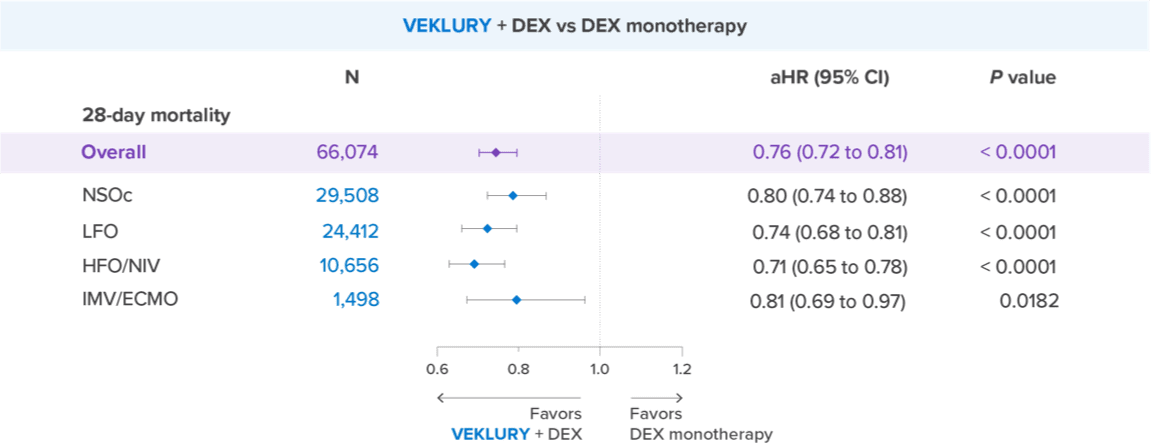
aHR=adjusted hazard ratio; DEX=dexamethasone; ECMO=extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; HFO=high-flow oxygen; IMV=invasive mechanical ventilation; LFO=low-flow oxygen; NIV=noninvasive ventilation; NSOc=no supplemental oxygen charges.
14-day mortality risk was also statistically significant for all supplemental oxygen requirements3,10
Overall, a 26% reduction in mortality risk was observed for patients treated with VEKLURY + dexamethasone within 2 days of admission compared to dexamethasone alone; aHR: 0.74 (95% CI, 0.69 to 0.78); P < 0.0001; n=66,074.
NSOc: 21% reduction; aHR: 0.79 (95% CI, 0.72 to 0.87); P < 0.0001; unadjusted: 5.6% vs 6.1%; n=29,508
Low-flow oxygen: 30% reduction; aHR: 0.70 (95% CI, 0.64 to 0.77); P < 0.0001; unadjusted: 6.1% vs 7.7%; n=24,412
High-flow oxygen/NIV: 31% reduction; aHR: 0.69 (95% CI, 0.62 to 0.76); P < 0.0001; unadjusted: 12.7% vs 15.7%; n=10,656
IMV/ECMO: 22% reduction; aHR: 0.78 (95% CI, 0.64 to 0.94); P = 0.0102; unadjusted: 23.5% vs 27.1%; n=1498
“…our study highlights that the addition of [VEKLURY] to dexamethasone is associated with a significant survival benefit compared to dexamethasone without [VEKLURY] use.”
Use of VEKLURY + corticosteroids was associated with reduced mortality risk across all oxygen subgroups vs corticosteroids alone3,11
An additional propensity score–matching sensitivity analysis was performed to compare effectiveness of VEKLURY + corticosteroid (including prednisone, prednisolone, methylprednisolone, hydrocortisone, and dexamethasone) vs corticosteroid monotherapy.
Mortality at Day 28: VEKLURY + corticosteroids vs corticosteroids alone (December 2021–April 2023)

reduced mortality risk was observed with VEKLURY + corticosteroids in the overall population; aHR: 0.76 (95% CI, 0.72 to 0.80), P < 0.0001; n=78,208
VEKLURY + corticosteroids reduced the risk of death across all supplemental oxygen subgroups vs corticosteroids alone
28-Day Mortality
NSOc: 19% reduction; aHR: 0.81 (95% CI, 0.75 to 0.87); P < 0.0001; n=35,642
Low-flow oxygen: 29% reduction; aHR: 0.71 (95% CI, 0.66 to 0.77); P < 0.0001; n=27,928
High-flow oxygen/NIV: 26% reduction; aHR: 0.74 (95% CI, 0.68 to 0.81); P < 0.0001; n=12,794
IMV/ECMO: 19% reduction; aHR: 0.81 (95% CI, 0.70 to 0.94); P = 0.0058; n=1844
14-Day Mortality
Overall population: 25% reduction; aHR: 0.75 (95% CI, 0.71 to 0.79); P < 0.001; n=78,208
NSOc: 20% reduction; aHR: 0.80 (95% CI, 0.74 to 0.87); P < 0.0001; n=35,642
Low-flow oxygen: 31% reduction; aHR: 0.69 (95% CI, 0.63 to 0.75); P < 0.0001; n=27,928
High-flow oxygen/NIV: 26% reduction; aHR: 0.74 (95% CI, 0.67 to 0.82); P < 0.0001; n=12,794
IMV/ECMO: 24% reduction; aHR: 0.76 (95% CI, 0.64 to 0.91); P = 0.0021; n=1844
View the real-world evidence published in Clinical Infectious Diseases
Important Safety Information
Important Safety
Information and Indication
Tap for Important Safety Information, including contraindication for history of clinically significant hypersensitivity to VEKLURY.
VEKLURY is indicated for the treatment of COVID-19 in adults and pediatric patients (birth to <18 years of age weighing ≥1.5 kg), who are hospitalized, or not hospitalized, with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 and are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death.
Contraindication
- VEKLURY is contraindicated in patients with a history of clinically significant hypersensitivity reactions to VEKLURY or any of its components.
Warnings and precautions
- Hypersensitivity, including infusion-related and anaphylactic reactions: Hypersensitivity, including infusion-related and anaphylactic reactions, has been observed during and following administration of VEKLURY; most reactions occurred within 1 hour. Monitor patients during infusion and observe for at least 1 hour after infusion is complete for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity as clinically appropriate. Symptoms may include hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, bradycardia, hypoxia, fever, dyspnea, wheezing, angioedema, rash, nausea, diaphoresis, and shivering. Slower infusion rates (maximum infusion time of up to 120 minutes) can potentially prevent these reactions. If a severe infusion-related hypersensitivity reaction occurs, immediately discontinue VEKLURY and initiate appropriate treatment (see Contraindications).
- Increased risk of transaminase elevations: Transaminase elevations have been observed in healthy volunteers and in patients with COVID-19 who received VEKLURY; these elevations have also been reported as a clinical feature of COVID-19. Perform hepatic laboratory testing in all patients (see Dosage and administration). Consider discontinuing VEKLURY if ALT levels increase to >10x ULN. Discontinue VEKLURY if ALT elevation is accompanied by signs or symptoms of liver inflammation.
- Risk of reduced antiviral activity when coadministered with chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine: Coadministration of VEKLURY with chloroquine phosphate or hydroxychloroquine sulfate is not recommended based on data from cell culture experiments, demonstrating potential antagonism, which may lead to a decrease in the antiviral activity of VEKLURY.
Adverse reactions
- The most common adverse reaction (≥5% all grades) was nausea.
- The most common lab abnormalities (≥5% all grades) were increases in ALT and AST.
Dosage and administration
- Administration should take place under conditions where management of severe hypersensitivity reactions, such as anaphylaxis, is possible.
- Treatment duration:
- For patients who are hospitalized, VEKLURY should be initiated as soon as possible after diagnosis of symptomatic COVID-19.
- For patients who are hospitalized and do not require invasive mechanical ventilation and/or ECMO, the recommended treatment duration is 5 days. If a patient does not demonstrate clinical improvement, treatment may be extended up to 5 additional days, for a total treatment duration of up to 10 days.
- For patients who are hospitalized and require invasive mechanical ventilation and/or ECMO, the recommended total treatment duration is 10 days.
- For patients who are not hospitalized, diagnosed with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, and are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death, the recommended total treatment duration is 3 days. VEKLURY should be initiated as soon as possible after diagnosis of symptomatic COVID-19 and within 7 days of symptom onset for outpatient use.
- Testing prior to and during treatment: Perform hepatic laboratory and prothrombin time testing prior to initiating VEKLURY and during use as clinically appropriate.
- Renal impairment: No dosage adjustment of VEKLURY is recommended in patients with any degree of renal impairment, including patients on dialysis. VEKLURY may be administered without regard to the timing of dialysis.
Pregnancy and lactation
- Pregnancy: Available clinical trial data for VEKLURY in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes following second- and third-trimester exposure. There are insufficient data to evaluate the risk of VEKLURY exposure during the first trimester. Maternal and fetal risks are associated with untreated COVID-19 in pregnancy.
- Lactation: VEKLURY can pass into breast milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for VEKLURY and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from VEKLURY or from an underlying maternal condition. Breastfeeding individuals with COVID-19 should follow practices according to clinical guidelines to avoid exposing the infant to COVID-19.
Indication
VEKLURY is indicated for the treatment of COVID-19 in adults and pediatric patients (birth to <18 years of age weighing ≥1.5 kg), who are hospitalized, or not hospitalized, with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 and are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death.
Please see full Prescribing Information for VEKLURY.
*Refer to the VEKLURY Prescribing Information for Dosage and Administration recommendations.
†Unmatched VEKLURY + dexamethasone patients were matched to dexamethasone monotherapy patients in another hospital of similar bed size within the specified caliper distance in the same age group and admission-month group using VEKLURY.
‡Other treatments administered at baseline for patients (across both study arms) included anticoagulants, convalescent plasma, and corticosteroids other than dexamethasone.
aHR=adjusted hazard ratio; ECMO=extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; IMV=invasive mechanical ventilation; NIV=noninvasive ventilation; NSOc=no supplemental oxygen charges.
PINC AITM is a trademark of Premier, Inc. (formerly Premier Healthcare Database).
